Drynaria quercifolia or more commonly known as the Oak-leaf fern is a "basket fern" belonging to the Polypodiaceae family .The reason for its common name of "oak leaf" as the nest fronds resemble the leaves of Oaks. They are a terrestrial fern found among rocks in crevices,shelves or in the soil among boulders also epiphytic on tree trunks in open forests and rainforests. Drynaria quercifolia is native to western Australia as well as India, Southeast Asia, Malaysia, Indonesia, the Philippines and New Guinea. This species of fern is characterised imparticularly by having "wooly" rhizomes.
Not threatened
The Rhizomes are 2cm thick and wooly. The scales are a dark brown to ginger in colour and are 20-25mm long and 0.7-2.5mm wide and soft. Stipes are winged at the base and lamina are not separated into distinct leaflets.Sori are round and circular in shape. Spores 37.5-55um long,22.5-37.5um wide. Fronds are both fertile and sterile. The veins are prominent and easily visible (Flora base).
Drynaria quercifolia reproduces through spores, is not poisonous but is used frequently as a medicine in many cultures and has many medicinal purposes.
The fossil record of Drynaria and drynarioids is not very well documented due to the typically poor preservation of fossils recovered. Previous fossil species assigned to Drynaria include Drynaria astrostigma. The arrangement and type of their sori, however, indicate that they are members of the family Matoniaceae instead.
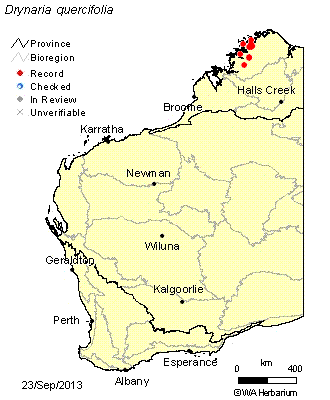
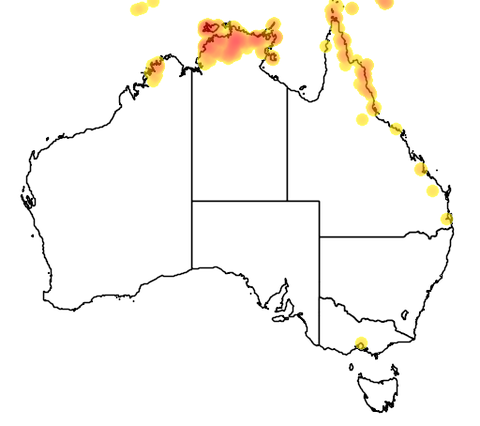
In open forest, rainforest margins and in dry rainforest.
Drynaria quercifolia is benefitial to humans as it has many medicinal values. A recent experiment conducted shows that the bioactive compounds from the rhizome of Drynaria quercifolia can be used to screen the antibacteril activuty against infectious diseases causing bacetrial pathogens. Some of the diseases in which this fern will hopefully be bale to work against are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Proteus mirabilis (Mithraja et al , 2012).In many native tribes the various parts of the fern are used to cure various sicknesses and symptoms. The plant is anthelmintic which helps expel worms and parasites from the body. The fronds can be used for coughs and to reduce swelling. The rhizomes have various uses. As a tonic it acts as an astringent to bowels and peeled rhizomes chewed is taken in scanty urination (Yusuf et al,2009).


Recent comments